Part 1: What is Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber?
Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) is a random chlorinate obtained through the chlorination of polyethylene. It can also be viewed as a binary copolymer of ethylene, vinyl chloride, and 1,2-dichloroethylene. When the chlorine content in CPE is below 20%, its elasticity diminishes, and its properties approach those of polyethylene. When the chlorine content exceeds 45%, its polarity increases, elasticity is lost again, and its properties resemble Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). Consequently, CPE products are generally categorized into four main types: Type A CPE, Type B CPE, Type C CPE, and HCPE.
Based on differences in chlorine content and residual crystallinity, Type A and Type C CPE are classified as resin-type CPEs, while Type B CPE belongs to the rubber-type CPE category. Since Type B CPE is predominantly a saturated rubber, it is also referred to as Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber (CM). For Type B CPE to function as a non-crystalline elastomer, a chlorine content of 30-40% is optimal. This article primarily focuses on exploring and sharing applications related to Type B CPE (CM), providing insights valuable for any Rubber compound manufacturer working with this material.
Part 2: Properties of Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber (CM)
- Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of CM are closely related to the base rubber grade, formulation, and production process. Being a polar material containing chlorine, its mechanical properties are also significantly influenced by ambient temperature. Its performance is comparable to that of commonly used Polychloroprene Rubber (CR).
| Property | Pure Rubber | Compound Rubber |
| Tensile Strength / MPa | 7~12 | 4~25 |
| Elongation at Break / % | 400~900 | 100~800 |
| Permanent Set at Break / % | 20~250 | 10~250 |
| Shore A Hardness / HA | 40~80 | 50~90 |
| Tear Strength / (N·mm⁻¹) | 3~10 | 3~20 |
- Dielectric Properties
Unsaturated CM has a high volume resistivity. However, after vulcanization, the volume resistivity decreases, and the dielectric constant and dielectric loss increase. This property is particularly relevant for applications like cable sheathing in the wire and cable industry.
| Property | Pure Rubber | Compound Rubber |
| Volume Resistivity / (Ω·cm) | (1~70)×10¹² | 1×10⁷ – 8×10¹⁴ |
| Dielectric Constant ε | 4.5~7.0 | 5.0~10.0 |
| Dielectric Loss tanδ | 0.008~0.08 | 0.03~0.35 |
| Dielectric Strength / (kV/mm) | 18~25 | 16~20 |
- Heat Aging Resistance
The molecular chain of CM has a linear saturated structure, granting it excellent resistance to hot air aging, making it a rubber material with excellent heat aging resistance. Its heat resistance surpasses that of many general-purpose rubbers (e.g., NR, SBR, BR, CR) and is comparable to EPDM. - Ozone, Light, and Weather Resistance
Similarly, the saturated molecular chain structure imparts outstanding resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and atmospheric weathering, making it suitable for long-term use in outdoor and ozone-rich environments. A detailed CM rubber vs EPDM weather resistance comparison often shows CM performing exceptionally well. - Low-Temperature Resistance
The brittle temperature of pure CM vulcanizates is similar to that of polyethylene, reaching -70°C to -80°C. However, the type and amount of plasticizers added in the compound formulation significantly impact the low-temperature performance of the final mix. - Oil and Chemical Resistance
CM exhibits superior resistance to mineral oils. Higher chlorine content generally correlates with better oil resistance. Vulcanizates with 35% chlorine content have oil resistance similar to general-purpose Nitrile Rubber (NBR), hence CM is the foundation for a high-performance Oil Resistant Rubber compound. CM is chemically inert and possesses strong resistance to acids, alkalis, and salts. Understanding how to design oil resistant CM rubber formula is key for specific applications. - Flame Retardancy
As a chlorine-containing polymer, CM inherently possesses a baseline level of flame retardancy. Incorporating appropriate synergistic flame retardants into the formulation can significantly enhance its flame-retardant properties, which is crucial for developing a High flame retardant CM cable compound formula.
Part 3: Products and Applications of Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber (CM)
Applications
| Application Area | Primary Purpose |
| Used as Specialty Synthetic Rubber | Improve heat stability, weather resistance, ozone resistance, chemical resistance, oil resistance, acid resistance, and flame retardancy for special rubber products such as wires & cables, automotive hoses, industrial hoses, sealing rings, gaskets, and linings. Improve the flexibility of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) foldable displays. |
| Blended with Natural Rubber (NR) | Improve the weather resistance, ozone resistance, and colorability of NR. |
| Blended with Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Improve the tensile strength, modulus, hardness, and tear strength of SBR; improve the oil resistance, heat aging resistance, and ozone resistance of SBR. |
| Blended with Butadiene Rubber (BR), Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR), and SBR | Improve the cell structure and distribution in the foaming system of shoe soles; enhance compatibility during mixing; ensure uniform mixing between foamed and non-foamed rubber. |
| Blended with Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) | Eliminate roll sticking during mixing; improve tensile strength, modulus, and hardness of finished products like wires & cables, automotive rubber parts, and waterproofing membranes; improve oil resistance, adhesion, and processing performance. |
| Blended with Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) | Improve tensile strength, modulus, hardness, and tear strength of finished products like automotive hoses, oil delivery hoses, engine seals, and molded rollers; improve weather resistance and elastic heat build-up properties; significantly improve ozone resistance. |
| Blended with Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Improve modulus, tear strength, and ozone resistance of finished products like flame-retardant conveyor belts, cables, mine air ducts, waterproofing membranes, and adhesives; eliminate mill sticking during mixing; significantly extend storage time. |
| Blended with NR and CR | Improve component compatibility in rubber systems for railway vehicle parts like air springs, air ducts, and dust covers; improve processing flowability, weather resistance, fatigue/aging resistance, and flame retardancy. |
Part 4: Principles for Material Selection in CM Compound Formulation
01. Selection of Base Rubber Grade
The key properties of CM base rubber are primarily determined by two parameters: Chlorine Content and Mooney Viscosity.
- Chlorine Content
Commercially available CPE grades typically range from low to high chlorine content: 25%, 30%, 35% (36%), 40%, 42%. Chlorine content is closely linked to flame retardancy, oil resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and elasticity.- For general requirements without specific demands, grades with 35% (36%) chlorine content are commonly used.
- For better flame retardancy or oil resistance, choose grades with 40% or 42% chlorine.
- For improved cold resistance or low-temperature performance, opt for grades with 25% or 30% chlorine.
- Mooney Viscosity
The Mooney Viscosity (ML(1+4) @125°C) of CM rubber typically ranges between 45 and 100. Higher Mooney viscosity indicates a higher molecular weight, generally leading to higher mechanical strength. However, excessively high Mooney viscosity can make extrusion processing very difficult. Due to CM’s high filler acceptance, Custom Rubber compound Manufacturers China like SaneZen Group can design formulations to meet various performance requirements.
02. Curing System
Currently, five curing systems are industrially applied for CM vulcanization:
- Organic Peroxide System
- Thiadiazole Derivative System
- Dimercapto-s-triazine System
- Thiourea System
- Electron Beam Radiation Curing
Generally, vulcanizates using the organic peroxide system exhibit better heat resistance and higher elasticity, though tear resistance might be slightly lower (this can be mitigated using co-agents like Si69). Radiation crosslinking can enhance surface hardness and heat resistance. Vulcanizates from the other three (thiadiazole, triazine, thiourea) systems typically show higher permanent set and poorer elasticity but offer better tear resistance.
03. Plasticizer System
Based on market usage trends, the peroxide curing system is widely adopted. Furthermore, due to the presence of polar chlorine ions, ester-based plasticizers are most suitable for CM. Appropriate plasticizers can lower the glass transition temperature (Tg) of CM vulcanizates, improving low-temperature performance and also enhancing processability.
- For heat-resistant formulations, TOTM is often chosen.
- For low-temperature resistant formulations, DOS is common.
- Considering cost, a combination of two or more plasticizers is often used.
Sanepar 756 plasticizer from SaneZen Group, a leading Rubber plasticizer Manufacturers China, considering the characteristics of various plasticizers on the market, features a flash point of 209°C and a pour point of -78°C. It satisfies the low-temperature flexibility of the compound without compromising its heat resistance.
Typical properties:
| Item | Testing method | Unit | Technical Data | Results |
| Appearance | GB/T 1664-1995 | — | Transparency | Transparency |
| Colour | GB/T 605-2006 | APHA | ≤30 | 21 |
| Content | GB/T 9722-2006 | % | ≥99.2 | 99.6 |
| Acid Value | GB/T 1668-2008 | mgKOH/g | ≤0.2 | 0.027 |
| kinematic viscosity(40℃)* | GB/T 265-1988 | mm2/s | — | 20.7 |
| Heat Loss | GB/T 6283-2008 | % | ≤0.15 | 0.02 |
| Relative density (25/25℃) | GB/T 4472-2011 | g/cm3 | 1.04~1.06 | 1.05 |
| Pour Point | GB/T 3535-2006 | ℃ | — | -78 |
| Refractive index(* 25/25℃) | GB/T 6488-2008 | — | 1.441~1.442 | 1.441 |
| Flash Point | GB/T 1671-2008 | ℃ | — | 209 |




04. Filler System
CM is a synthetic rubber suitable for high filler loading. Compared to other general-purpose rubbers, carbon black is the most effective reinforcing filler for CM, but semi-reinforcing furnace (SRF) blacks with lower heat generation are preferred. For enhancing flame retardancy and improving oil resistance, small amounts of silica can be added.
Since increasing carbon black loading raises the compound’s Mooney viscosity, large quantities of mineral fillers are often considered. The fineness of mineral fillers significantly impacts the mechanical properties of the vulcanizate; hence, finer particle size fillers are typically selected.
The PF series of Nano Reinforcing Fillers from SaneZen Group a prominent Rubber Functional filler Manufacturers China and Rubber reinforcing filler Manufacturers China, featuring surface treatment, offer excellent reinforcement, high whiteness, good dispersion within the compound, and superior electrical insulation properties! The strategic nano filler apply in CPE rubber compound delivers significant performance enhancements.
Typical properties
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Chemical Analysis | ||||
| %+325 mesh (>45 um) | 0.01% | Regular whiteness GEM | 71 | SiO₂ | 50.30% |
| Median particle size D10 (nm) | 73 | PH (aqueous solution) AFS113-87-S | 5.95 | Al₂O₃ | 34.50% |
| Median particle size D50 (nm) | 153 | Moisture content AFSC-566 | 0.91% | TiO₂ | 1.60% |
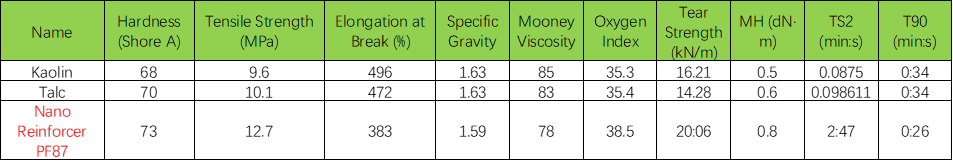
Specifically, the application of PF87 in CPE cable formulations demonstrates superior performance compared to formulations using common inorganic fillers like kaolin or talc. Benefits include enhanced product performance (increased strength, lower specific gravity, Oxygen Index increased by 3 points), improved mixing process (lower Mooney viscosity, longer scorch time, and shorter optimal cure time), offering a Cost effective high performance rubber filler solution.
05. Other Additives
Similar to other chlorine-containing polymers, CM can undergo dehydrochlorination when exposed to heat, ozone, UV light, or certain active chemical groups. This can lead to reactions ultimately terminating chemical crosslinks and degrading the rubber. Therefore, it is essential to add heat stabilizers, acid acceptors, lubricants, and antioxidants to the formulation.

SaneZen Group: Your Expert CPE Rubber Compound Manufacturer and Innovation Partner
SaneZen Group is an innovative one-stop CPE Rubber compound manufacturer and a leading Customized rubber compound manufacturer. We not only provide specialized custom compound production services but also supply a comprehensive range of rubber raw materials, positioning us as reliable Rubber Functional filler Manufacturers China and Rubber plasticizer Manufacturers China. Our expertise and manufacturing capabilities ensure we deliver significant value to our customers by enabling the development of high-performance, cost-effective rubber products tailored to specific needs, including advanced Oil Resistant Rubber compound and specialized cable compounds.
