Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer produced by the selective hydrogenation of carbon-carbon double bonds in the nitrile rubber molecular chain. This hydrogenation process significantly enhances the rubber’s heat resistance, ozone aging resistance, and mechanical strength, while maintaining excellent oil resistance and compression set resistance. This paper systematically elaborates on the basic characteristics of HNBR, focusing on analyzing its performance under extreme working conditions such as high heat, high pressure, and corrosive media. From the perspectives of material blending, functional additives, and process optimization, it reviews technical pathways for further improving its overall performance. Simultaneously, incorporating the professional production capability and product portfolio of SaneZen Group’s Anhui Lixin Plant in the HNBR field, this paper introduces its HNBR series grades and their application advantages in high-end sealing fields, providing theoretical basis and technical reference for the development of high-performance seals used in oilfield drilling tools, aerospace, and industrial equipment. This includes insights from leading HNBR compound Manufacturers China and HNBR compound Suppliers China.
2. Basic Characteristics and Advantages of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber is produced via catalytic hydrogenation of nitrile rubber. The significant reduction of unsaturated bonds in its molecular chain makes it markedly superior to traditional NBR in terms of heat resistance, aging resistance, and mechanical properties, specifically demonstrated in:
2.1 Exceptional High-Temperature Resistance
Long-term service temperature can reach above 150°C, with short-term heat resistance limits exceeding 160°C. Some modified grades can maintain stable performance in 180°C environments, making it a prime Oil resistant high temperature rubber compound.
2.2 Excellent Ozone and Weather Aging Resistance
The saturated structure after hydrogenation effectively resists ozone erosion, making it suitable for outdoor and poorly ventilated enclosed equipment.
2.3 Good Resistance to Oils and Chemical Media
Retains acrylonitrile polar groups, offering good stability against lubricating oils, diesel fuel, and acidic/alkaline media.
2.4 High Mechanical Strength and Tear Resistance
Typical tensile strength exceeds 20 MPa, with some reinforced compounds reaching 30 MPa.
2.5 Low Compression Set
Under test conditions of 150°C × 70 h, the compression set can be controlled below 30%, outperforming most rubber materials.
Therefore, HNBR has become an ideal base material for high-temperature and chemical-resistant seals, widely used in drilling equipment, automotive engine systems, and chemical processing equipment, serving as a key HNBR Compound for High performance rubber seals.
3. SaneZen Group Anhui Lixin Plant HNBR Product Portfolio and Performance Advantages
As a specialized rubber composite material manufacturing base under SaneZen Group, Anhui Lixin Plant possesses the following core advantages in the R&D and production of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber compounds:
3.1 Comprehensive Rubber Composite Capability
Covers over 33 rubber types, including Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber HNBR, providing a complete product line from base compounds to high-performance specialty compounds, positioning it as a leading HNBR compound Factory.
3.2 Extensive R&D and Production Experience
Boasts over 20 years of professional rubber R&D and production experience, with 26 specialized rubber composite production lines and an annual capacity of 150,000 tons, establishing it among top HNBR compound Manufacturers and HNBR compound Suppliers.
3.3 Dedicated Colored Rubber Compound Production Line
Operates an independent colored rubber composite material factory to meet diverse customer needs for color identification and aesthetic design, even for Customized HNBR compound.
3.4 Mature Formulation System
Possesses 10,000+ proven rubber composite material formulations, enabling the provision of Customized HNBR compound formulations based on specific customer operating conditions.



See this video to get to know about our factory :
In the field of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber, the HNBRXX series products launched by Anhui Lixin Plant feature the following grades and typical properties, demonstrating their capability as a supplier of HNBR compound for high performance seals:
Grade Hardness (Shore A) Tensile Strength (MPa) Elongation at Break (%) Typical Application
| Grade | Hardness (Shore A) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Typical Application |
| HNBR45 | 45–50 | ≥10.79 | ≥520 | Low-pressure seals, hoses |
| HNBR55 | 55–60 | ≥13.32 | ≥379 | Oil seals, O-rings |
| HNBR65 | 65–70 | ≥17.01 | ≥365 | Dynamic seals, valve stem seals |
| HNBR75 | 75–80 | ≥18.67 | ≥336 | High-pressure rotary seals |
| HNBR85 | 85–90 | ≥20.16 | ≥211 | Extreme condition static seals |
This series of products performs excellently in heat aging resistance, oil medium resistance, and compression set resistance, making them suitable for manufacturing seals used in oilfield drilling tools, automotive turbocharger systems, air conditioning compressors, and other high-temperature, high-pressure, oil-immersion environments, often requiring Oil and heat resistant rubber compound supplier expertise.
4. Technical Pathways for Enhancing HNBR Performance
4.1 Blending Modification with Special Polymer Materials
Blending is an important method to expand the performance window of HNBR and achieve multifunctionality:
4.1.1 Blending with Fluoroelastomer
Fluoroelastomer offers excellent high-temperature and chemical resistance, but has poor low-temperature performance and elasticity. Blending HNBR with FKM balances heat resistance and elasticity, suitable for a wide temperature range from -40°C to 190°C, with low volume change rate in hot oil environments.
4.1.2 Blending with Polyimide
Polyimide is a high-performance engineering plastic with a long-term service temperature exceeding 260°C. Blending a small amount of polyimide with HNBR significantly increases the material’s heat resistance上限 and insulation properties, suitable for high-power electrical equipment seals and ultra-high temperature static sealing applications.
4.1.3 Blending with EPDM
EPDM has excellent ozone and weather resistance, but poor oil resistance. Blending the two can balance oil resistance and weather resistance to some extent, suitable for components requiring both oil resistance and outdoor aging resistance.
4.2 Reinforcement and Functionalization with Functional Additives
Rational selection of functional additives is key to controlling HNBR performance:
4.2.1 Nano Reinforcement Materials
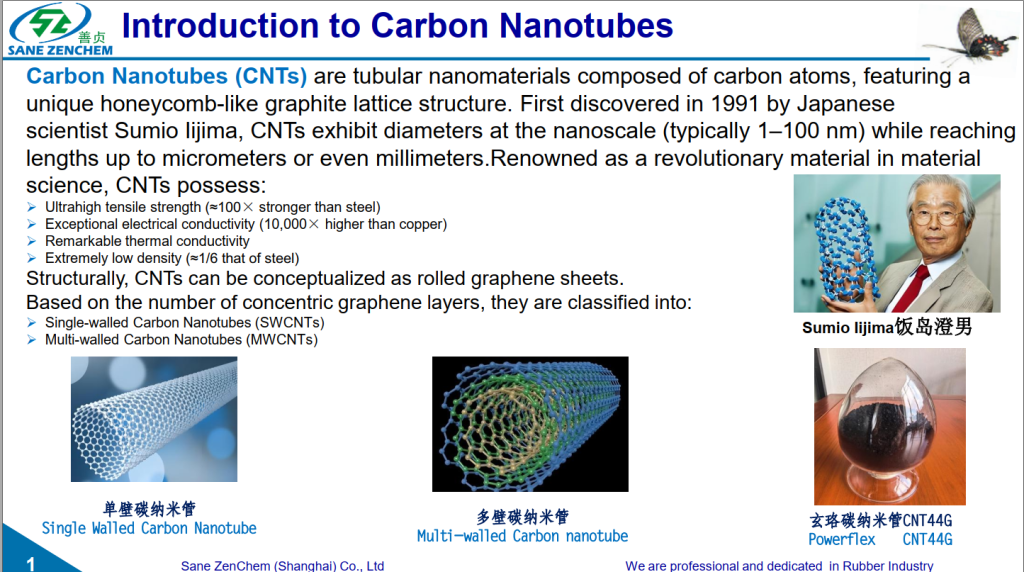
- Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene: As efficient thermal conductive and reinforcing agents, they can significantly increase the compound’s thermal conductivity, avoiding local overheating, while improving modulus, and tear strength. This is particularly true for Conductive Carbon Nanotube materials and specialized High conductivity Carbon Nanotube masterbatch, which contribute significantly to High Thermal Conductive Rubber Composite development. Studies show that adding 2-5 phr graphene can increase the heat resistance temperature of HNBR by 25-35°C, representing a Technology to improve heat life of rubber compound.
- Carbon Nanotubes (CNT): The GreenThinking® CNT44G series Multi walled Carbon Nanotube developed by SaneZen Group features high dispersibility and easy processing, effectively enhancing the mechanical properties and functional characteristics of HNBR compounds. As a highly engineered Conductive Carbon Nanotube, it offers superior performance:
- Conductive/Antistatic Properties: Very low addition levels (1-5 phr) of this Conductive Carbon Nanotube can significantly reduce the volume resistivity of the compound, achieving antistatic or even electromagnetic shielding functions, meeting requirements of standards like ATEX.
- Mechanical Enhancement Effect: The nanofiber structure of this Multi walled Carbon Nanotube effectively disperses stress, significantly improving the modulus, tensile strength, tear strength, and wear resistance of HNBR. Experiments show that adding 3 phr CNT44G can increase the tear strength by approximately 28%.
- Thermal Conductivity Optimization: The high thermal conductivity of CNT44G helps rapid heat dissipation within the compound, increasing thermal conductivity by about 10.5% compared to traditional fillers at the same loading level.
- Processing Adaptability: The CNT44G series Multi walled Carbon Nanotube, available in masterbatch forms like the High conductivity Carbon Nanotube masterbatch, is developed specifically for the rubber industry and offers good dispersibility. It can be added directly in the initial mixing stage. The recommended dosage is 3-6 phr, adjustable based on specific performance requirements.
Modified Carbon Black and Silica: Surface modification improves their interfacial adhesion with rubber, enhancing strength while maintaining low heat build-up and compression set.

4.2.2 Cross-linking Enhancement Systems
- Magnesium Methacrylate: As an active co-agent in peroxide curing systems, it participates in building an ionic cross-linking network, significantly increasing crosslink density, thereby simultaneously improving heat resistance, strength, and compression set resistance.
- Multifunctional Curing Co-agents: Such as trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate, can further enhance the efficiency of peroxide curing and the stability of the cross-linked structure.
4.2.3 Special Reinforcing Fillers
- Boron Nitride: Possesses high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, suitable for sealing applications requiring high heat dissipation, contributing to High Thermal Conductive Rubber Composite solutions.
- Polyester Fiber and Asbestos Fiber: As short fiber reinforcement phases, they can improve the dimensional stability and puncture resistance of the compound, suitable for high-pressure reciprocating seal structures.
4.3 Curing Systems and Process Optimization
4.3.1 Curing System Selection
Peroxide curing systems form C-C crosslinks with high bond energy and good thermal stability, making them the preferred choice for high-temperature HNBR applications. Sulfur curing systems are suitable for applications requiring high dynamic fatigue performance, but their heat resistance is slightly inferior.
4.3.2 Composite Antioxidant System
Using composite antioxidants with both anti-thermal oxidation and anti-metal ion catalytic functions, such as a combination of quinoline and phosphite types, can significantly extend the service life of HNBR in high-temperature air, a key Technology to improve heat life of rubber compound.
4.3.3 Pre-made Base Compounds and Masterbatch Process
By pre-preparing masterbatches with high additive loadings or using pre-made compound materials, uniform filler dispersion and process stability are ensured, improving product consistency and processing efficiency, beneficial for Customized HNBR compound formulations.
4.3.4 Thermal Barrier Structure and Interface Treatment
Using HNBR as the base material for thermal barrier layers in seal system design, combined with surface coatings or metal composite structures, can effectively block heat source conduction and protect secondary sealing elements.
5. Conclusion and Outlook
5.1 As a high-end derivative of nitrile rubber, Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR), by virtue of its hydrogenation-modified molecular structure, possesses outstanding heat resistance, ozone resistance, oil resistance, and mechanical strength, and has become one of the preferred materials for seals in demanding applications, supplied by various HNBR compound Manufacturers and HNBR compound Manufacturers Suppliers.
5.2 By blending with special polymers like fluoroelastomer and polyimide, composite compound systems with wider temperature ranges and more comprehensive functionalities can be constructed, meeting the complex performance requirements of extreme environments, a focus for developers of Customized HNBR compound formulations.
5.3 The development and application of new functional additives such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, and magnesium methacrylate provide multiple functional enhancement paths for HNBR, including reinforcement, thermal conductivity, and aging resistance, driving its development towards high performance and multifunctionality, including High Thermal Conductive Rubber Composite.
5.4 Optimizing the curing system, adopting composite anti-aging technology, and utilizing pre-made processes contribute to the long-term stable operation of HNBR compounds in high-temperature, high-pressure, and complex media environments, leveraging Technology to improve heat life of rubber compound.
With continuously increasing requirements for sealing technology in oil and gas extraction, aerospace, and new energy equipment, Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber, with its excellent comprehensive properties and flexible designability, will continue to hold a key position in the field of high-performance sealing. Professional rubber composite material manufacturers represented by SaneZen Group’s Anhui Lixin Plant, leveraging their complete HNBR product matrix, mature formulation systems, and professional production lines, will continue to provide global industrial customers with high-performance, high-reliability sealing solutions, solidifying their role as leading HNBR compound Manufacturers China and HNBR compound Suppliers China. Future research should further focus on multi-scale structure control of materials, establishment of life prediction models, and green sustainable manufacturing processes to promote the innovative application of HNBR materials in broader industrial scenarios.
